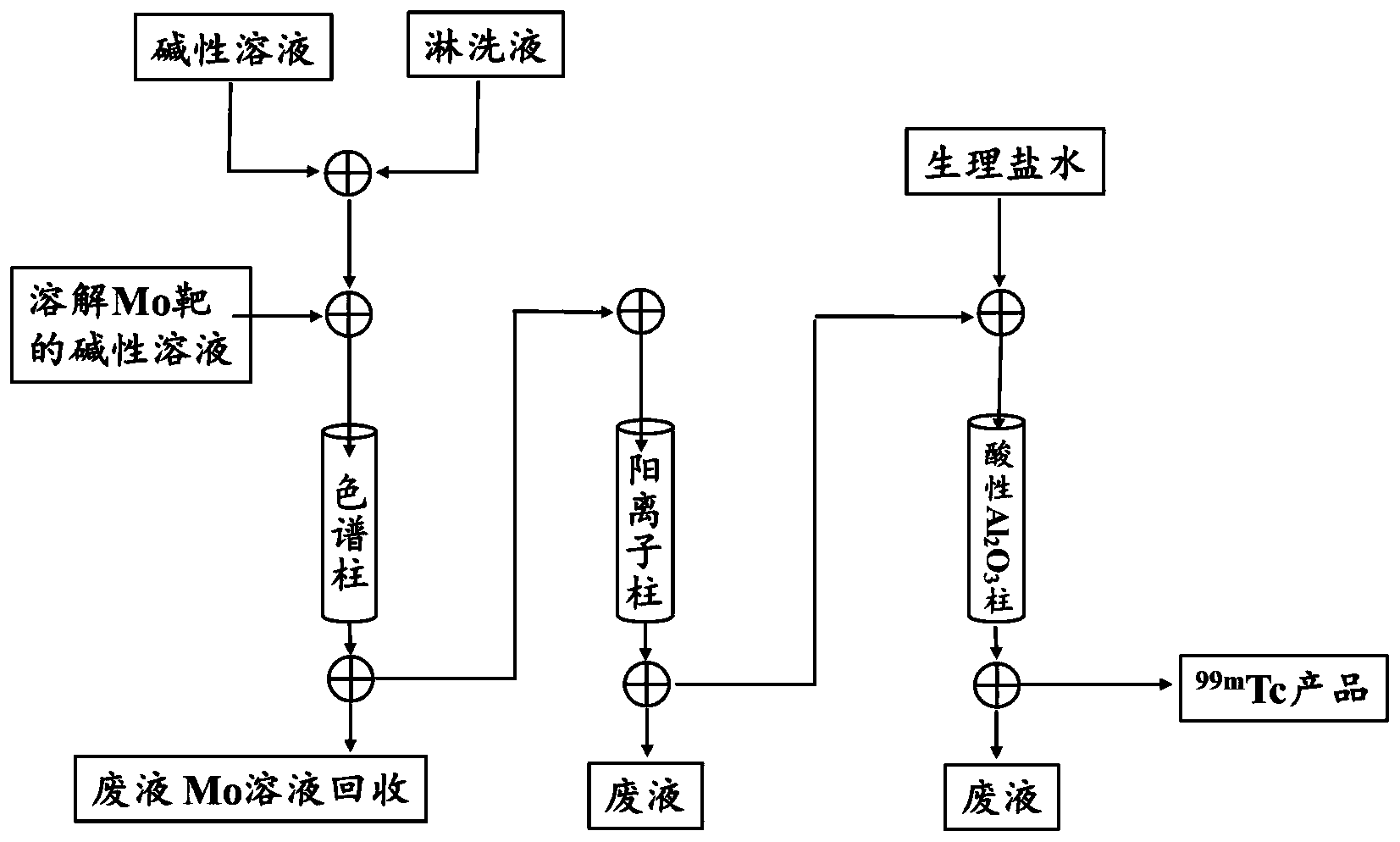
The invention discloses a device and a method for separating 99mTc from a large amount of Mo solution with low specific activity. The device includes a sample injection system, a column separation system, a column purification system and a product collection system connected in sequence; the column separation system includes a chromatographic separation column filled with polyethylene glycol resin, an injection pump connected with it and a waste liquid collection bottle; the column purification system includes two purification columns connected in sequence and the injection pump connected with the column. The device can be automatically controlled to effectively prevent radiation damage to operators. The separation process is easy to operate, and the chromatographic column and purification column are easy to replace, which can realize scale and commercialization.
The method uses column chromatography to directly enrich and separate 99mTc from Mo irradiated by accelerator, and the process is simple, the solution containing 99Mo is directly recycled and reused, less radioactive waste is generated, the environmental pollution caused by radioactivity is reduced, and the economic benefit is high.
Radioisotope plays an increasingly important role in the diagnosis and clinical treatment of diseases. At present, the most widely used radioisotope in nuclear medicine is 99mTc (T1 / 2 = 6h) of 99Mo (T1 / 2 = 66h), because 99mTc has the advantages of pure low-energy gamma ray (141kev) and appropriate half-life. The usage of 99mTc accounts for about 80% of all radioisotopes. There are 30-40 million times a year for nuclear medicine imaging diagnosis in the world. As the parent of 99mTc, the main source of 99mTc is to extract it from 235U fission products after irradiation of the reactor. The separation steps are complicated, which will produce large radioactive waste and pollute the environment, making the production cost of 99mTc high and the price high. On the one hand, most of these reactors are facing aging, poor operation stability or decommissioning, which leads to the shortage of radioisotopes, especially fission 99Mo. On the other hand, restrictions on the use of highly enriched uranium (HEU) with nuclear proliferation risks have led to a crisis in the supply of 99mTc.
The production of 99Mo based on accelerator or direct production of 99mTc has become an internationally recognized method, such as 99Mo produced by electron accelerator irradiation of 100mo. At the same time, based on the existing medical cyclotron proton accelerators, 99mTc can also be produced directly through the nuclear reaction of 100mo (P, 2n), thus the supply of 99mTc can be maintained. However, there are a lot of Mo isotopic carriers in 99Mo or 99mTc obtained by accelerator, which has the characteristics of low specific activity. At present, the main separation and purification methods of 99mTc based on accelerator production are column chromatography, solvent extraction, chemical precipitation and thermal chromatography.
In addition, 99Mo nuclides used in hospitals in China are all imported. Therefore, in order to realize the independent and large-scale supply of medical nuclides, it is of great significance to carry out the separation and purification of 99Mo and 99mTc based on accelerator production.
[1] 范芳丽;秦芝,一种从大量、低比活度Mo溶液中分离99mTc的装置及方法,CN111485123A, 2020



